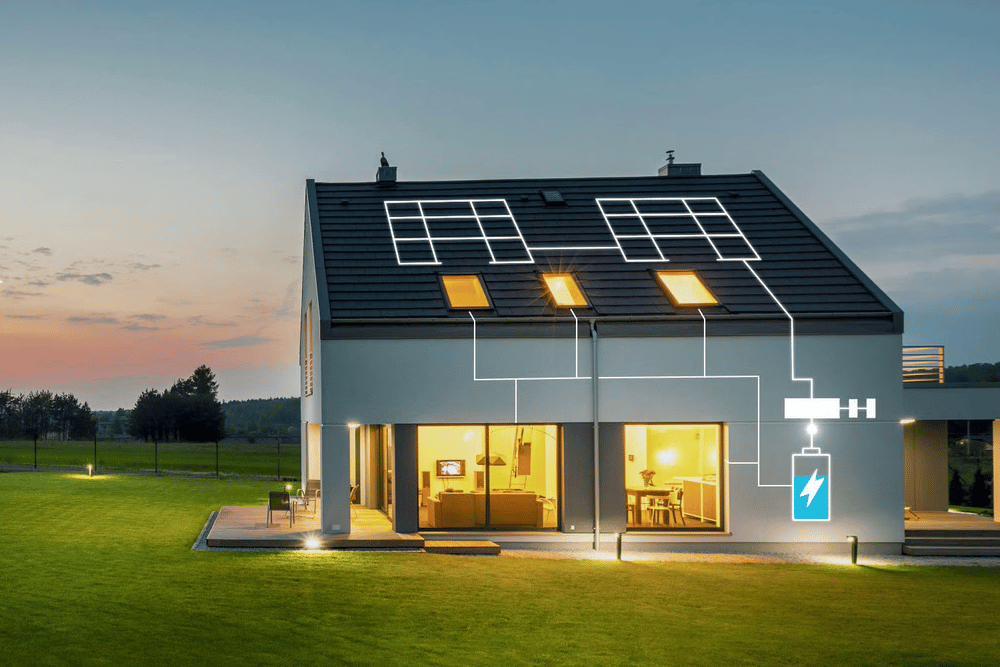
As home energy storage continues to evolve, we now have more options to meet our energy needs. Two common options are grid-tied systems and off-grid systems. When choosing the right energy configuration, it’s crucial to understand their differences, pros and cons.
Grid-connected system:
Stable and reliable: The grid-tied system connects your home grid to the public power network, allowing you to obtain stable power supply at any time.
Utilize public power: You can tap into power provided by the public power grid without relying on solar panels or other energy sources.
Suitable for urban environments: In cities or high-density residential areas, it may be inconvenient to install solar panels due to limited space, so grid-tied systems may be a more practical option.
Cost savings: You can reduce energy costs by selling excess energy back to the grid for a certain return.
Ease of Maintenance: Maintenance of public power networks is usually the responsibility of the local power company, making maintenance and repairs easier.
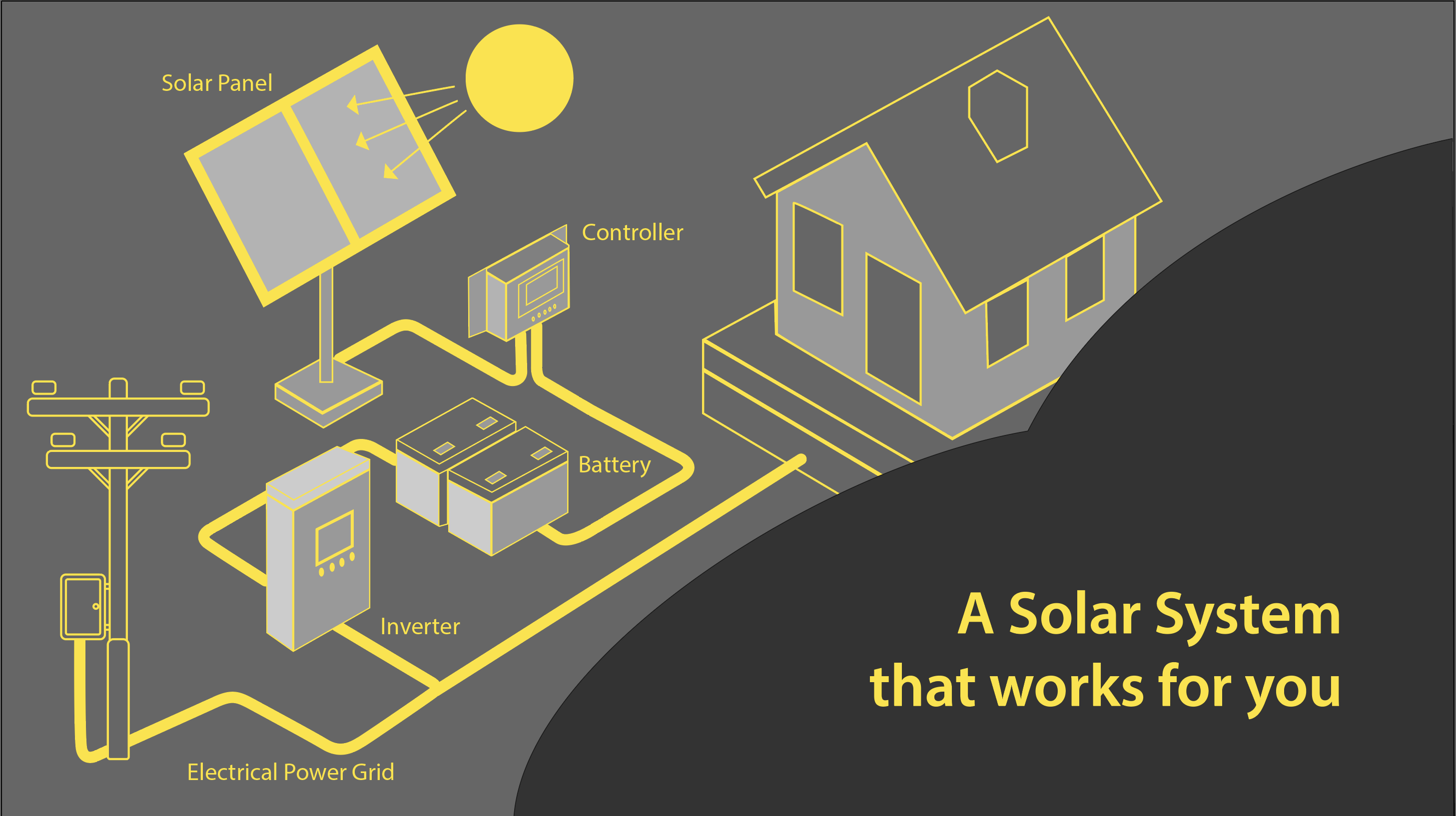
Off-grid systems:
Independently Powered: Off-grid systems do not rely on the public power grid, allowing you to continue supplying power in the event of a power outage or no public power supply.
Environmentally sustainable: By utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar or wind energy, off-grid systems enable an independent, environmentally friendly energy supply.
Remote area use: In remote areas or places where there is no public power supply, off-grid systems are ideal for meeting energy needs.
Independent Control: You have complete control to manage your energy generation and use to meet your home’s unique needs.
Contribute to environmental protection: By reducing your dependence on traditional energy, you make a positive contribution to environmental protection.
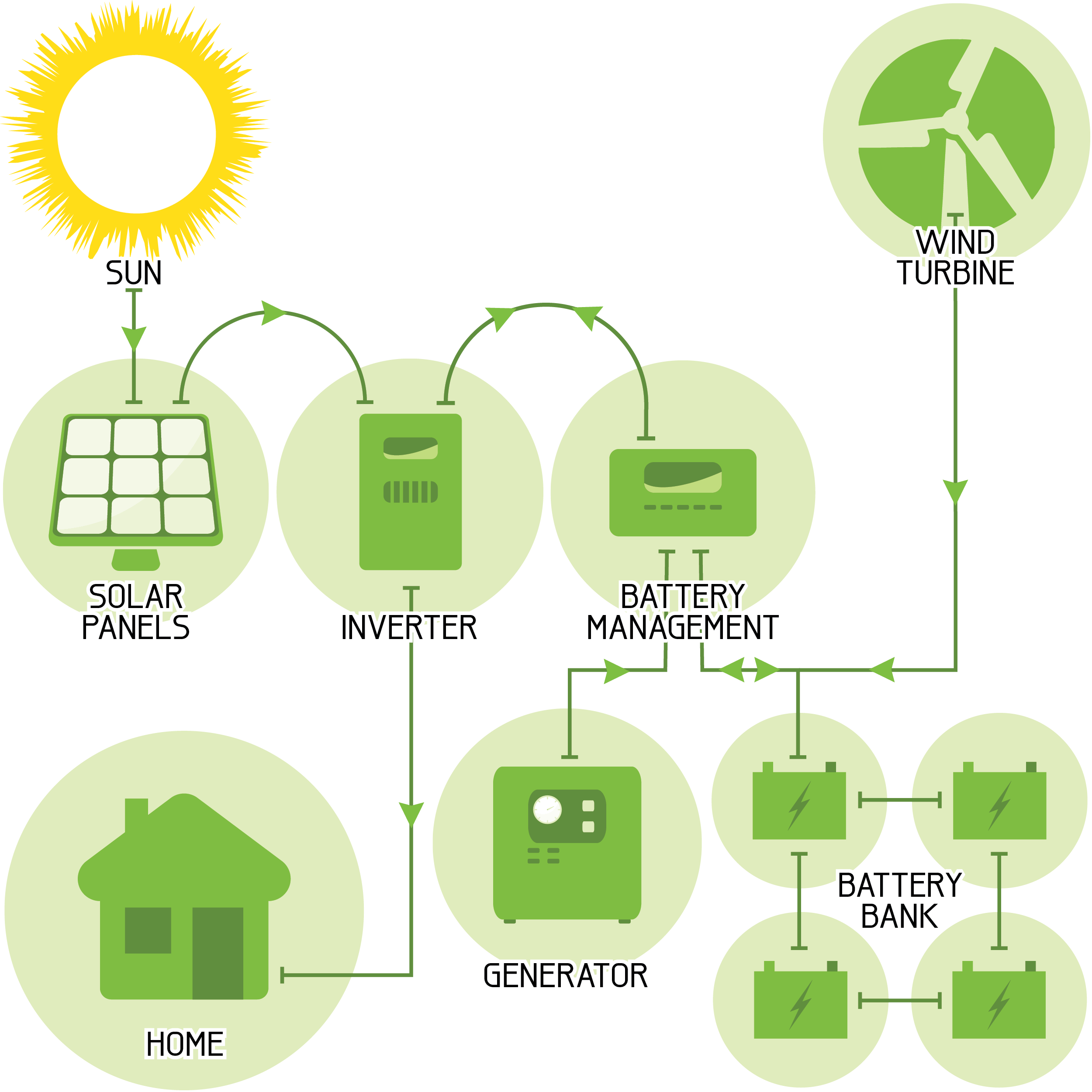
How to choose the right configuration:
- Analyze your needs: First, assess your home energy needs and lifestyle to determine how much energy you need and your usage patterns.
- Consider your budget: Knowing your budget will help determine whether you would prefer an affordable grid-tied system or a stand-alone off-grid system.
- Get professional advice: Speak with an energy expert or technician to get advice on the configuration that best suits your needs.
- All things considered: In some cases, a hybrid system that combines the advantages of on-grid and off-grid may be the best option.
Whether you choose a grid-tied or off-grid system, you’ll be provided with safe, reliable energy solutions to meet your home’s unique needs. Remember, it is crucial to do careful research and seek professional advice before making a decision.
If you want to build a 30 kWh solar system, it should include the following components:
- Solar Panel (Photovoltaic Module): This is the core component of the system and is responsible for converting sunlight into electricity. A 30 kWh system typically requires a certain number of solar panels to generate enough power.
- Inverter: An inverter converts direct current (DC) power from solar panels to alternating current (AC) power for use by household appliances.
- Battery energy storage system: used to store excess solar power to continue supplying power at night or in low light conditions. Please choose a high-quality home energy storage battery with a battery management system (BMS). This system can control and monitor the battery’s charge and discharge process to ensure the safe and efficient operation of the 30 kWh solar system.
- Safety switches and fuses: Provide electrical safety protection for the system from overcurrent or other electrical problems.
- Cables and Wiring: Used to connect all components and ensure that power can flow smoothly.
- Bracket or mounting system: A structure used to mount solar panels, usually including brackets, struts, and mounting hardware.
- Monitoring system: used to monitor the performance and power output of the system in real time so that any problems can be discovered and resolved in a timely manner.
- Distribution box: Connects solar power to the home grid to ensure that the power can be used by household devices.
- Backup power system (such as generator): Optional to provide backup power when solar power is insufficient or storage power is exhausted.
Post time: Nov-03-2023