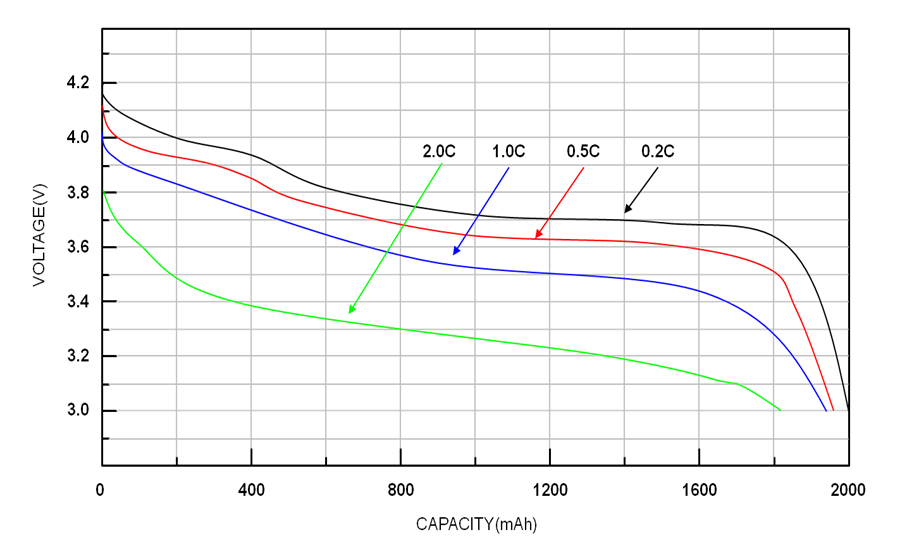
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their efficiency, reliability, and widespread application. Voltage and current are two critical parameters for evaluating and utilizing lithium batteries. They directly impact battery performance, efficiency, and safety. Understanding their differences and relationships helps ensure optimal battery use and stable device operation.
What Does Voltage Represent?
Voltage is one of the most important parameters of a lithium-ion battery, representing the potential difference between the two electrodes of the battery. It acts as the “driving force” that pushes electrons through an external circuit.
Unit of Voltage
Voltage is measured in volts (V), and the nominal voltage often represents the typical operating voltage of a battery.
What Are Common Lithium-Ion Battery Voltages?
- Single-cell lithium-ion batteries: Nominal voltage is typically 3.7V.Common models include 18650 and 21700 batteries, etc.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries: Nominal voltage is 3.2V.
- Fully charged: Voltage reaches approximately 4.2V.
- Fully discharged: Voltage ranges from 2.5V to 3.0V (discharging below this range may damage the battery).
Importance of Voltage
Voltage determines whether a device is compatible with a specific battery. Devices require a matched input voltage to operate correctly. Excessively high or low voltages may lead to device malfunction.
What Does Current Represent?
Current refers to the rate of electron flow through an external circuit, describing the battery’s ability to supply power to a device.
Unit of Current
Current is measured in amperes (A). For small devices, it’s often expressed in milliamperes (mA), while larger energy storage systems may use amperes (A) or even kiloamperes (kA).
Importance of Current
Current impacts the power output of the device and the discharge rate of the battery. Excessive current can lead to overheating and potential battery failure, while insufficient current may not meet the device’s power requirements.
The Relationship Between Voltage and Current
Voltage and current are related through Ohm’s Law:
I=V/R
- I: Current (A)
- V: Voltage (V)
- R: Resistance (Ω)
Under constant resistance, increasing the voltage leads to higher current. Similarly, the amount of current drawn can influence battery discharge efficiency and heat generation.
Interaction of Voltage and Current
- When current increases: More heat is generated within the battery, potentially affecting safety and lifespan.
- When voltage drops: If voltage falls too low, the device may stop functioning.
Differences Between Voltage and Current
|
Parameter |
Voltage |
Current |
| Definition | The potential difference between the two battery terminals, acting as the “force” driving electron flow. | The rate at which electrons flow through a circuit, representing the speed of energy transfer. |
| Unit | Volt (V) | Ampere (A) |
| Influencing Factors | Battery material, electrolyte, state of charge, etc. | External load, internal resistance, and device power requirements. |
| Role | Determines if the device can start and operate. | Determines the runtime and power output of the battery. |
| Measurement | Measured with a voltmeter to check the potential difference. | Measured with an ammeter to check the flow of current. |
Does Charging or Discharging Change a Lithium-Ion Battery’s Voltage?
Yes, the voltage of a lithium-ion battery changes with its State of Charge (SOC):
- During charging: Voltage gradually increases and stabilizes at around 4.2V when fully charged.
- During discharging: Voltage gradually decreases and approaches 2.5V when fully discharged.
This voltage variation reflects the progression of the battery’s internal chemical reactions, making it a critical parameter for estimating remaining battery capacity.
Relationship Between SOC, SOH, and Voltage
- SOC (State of Charge): Indicates the remaining battery capacity, directly related to voltage. Higher voltage typically corresponds to a higher SOC.
- SOH (State of Health): Reflects the battery’s health, affecting its maximum charge voltage and discharge stability.
- Role of Voltage: Voltage changes are a key indicator of SOC and SOH, helping monitor battery performance and predict lifespan.
Common Misconceptions About Voltage and Current
1. Is Higher Voltage Always Better?
No. High voltage may overload and damage devices. A matched input voltage is essential for proper device operation.
2. Does Higher Current Mean Better Performance?
Not necessarily. While higher current enables greater power output, excessive current can accelerate battery aging and increase the risk of overheating.
3. Are Voltage and Capacity Unrelated?
Incorrect. Battery capacity is the product of voltage and current:
Energy (Wh) = Voltage (V) × Capacity (Ah).
Thus, voltage directly impacts the total energy storage of the battery.
Conclusion
Voltage and current are essential parameters for assessing the performance of lithium-ion batteries. Voltage determines whether a device can operate, while current dictates the energy transfer rate and runtime. Understanding their relationship and differences is crucial for safe and efficient battery use. Proper knowledge of these parameters ensures optimal device operation and extends battery life.
Post time: Jan-02-2025