Oververhitting van de batterij is een belangrijk probleem dat kan optreden tijdens batterijgebruik, vooral bij een hoog vermogen of langdurig gebruik. Oververhitting kan niet alleen leiden tot een afname van de batterijprestaties, maar ook tot veiligheidsrisico's, zoals brand of explosie. Daarom is het cruciaal om de oorzaken, symptomen en preventiemethoden voor oververhitting van de batterij te begrijpen.de levensduur van de batterij verlengenen het verbeteren van de veiligheid.
Wat is oververhitting van de batterij?
Oververhitting van de accu verwijst naar de situatie waarbij de bedrijfstemperatuur van de accu het ontworpen veilige bereik overschrijdt. Elke accu heeft een optimaal bedrijfstemperatuurbereik. Wanneer de temperatuur dit bereik overschrijdt, kunnen de chemische reacties in de accu instabiel worden, wat leidt tot prestatievermindering en zelfs potentiële gevaren.
Gevolgen van oververhitting van de batterij
De gevolgen van oververhitting van de batterij kunnen zijn:
- Prestatievermindering:Oververhitting versnelt de veroudering van de batterij, waardoor de effectieve capaciteit afneemt en de gebruiksduur van de batterij korter wordt.
- Thermische Runaway (TR)Hoge temperaturen kunnen leiden tot thermische runaway in de batterij, wat kan leiden tot snelle temperatuurstijgingen, zwelling en zelfs brand of explosies.
- Batterijschade: Langdurige oververhitting kan de interne chemische samenstelling van de batterij beschadigen, waardoor lekkage ofbatterijvervorming.
Oorzaken van oververhitting van de batterij
De oorzaken van oververhitting van de batterij kunnen variëren, waaronder:
- Snel opladen of overladen: Snelladen genereert hoge stromen in de accu, wat leidt tot oververhitting. Als de laadstroom de capaciteit van de accu overschrijdt, stijgt de accutemperatuur snel.
- Batterij van slechte kwaliteit of defect:Oude batterijen of batterijen van slechte kwaliteit hebben een verhoogde interne weerstand, wat leidt tot hitteaccumulatie en oververhitting.
- Hoge buitentemperatuur:In warme omgevingen kan de batterij minder warmte afvoeren, waardoor de kans op oververhitting groter wordt.
- Onjuist gebruik of overmatige ontlading:Batterijen kunnen oververhit raken als ze te ver ontladen worden, vooral bij langdurige hoge belasting.
- Storing in het batterijbeheersysteem (BMS):Een storing in het batterijbeheersysteem kan ervoor zorgen dat de temperatuur en stroom niet goed worden bewaakt, wat oververhitting tot gevolg kan hebben.
Symptomen van oververhitting van de batterij
Veelvoorkomende symptomen van oververhitting van de batterij zijn:
Vervorming of zwelling:
Oververhitting verhoogt de interne druk, waardoor de behuizing van de batterij kan opzwellen of vervormen.
Geur of rook:
Oververhitte batterijen kunnen een onaangename geur of rook afgeven, wat kan wijzen op overmatige interne reacties.
Abnormaal hoge temperatuur:
De oppervlaktetemperatuur van de batterij is aanzienlijk hoger dan de normale bedrijfstemperatuur.
Verminderde laad- of ontlaadefficiëntie:
Oververhitting kan de prestaties van de batterij verminderen, wat leidt tot lagere laadsnelheden en een verminderde ontlaadcapaciteit.
Hoe voorkom je dat de batterij oververhit raakt?
- Gebruik de juiste oplader: Gebruik een lader die bij de batterij past om snelladen te voorkomen. Zorg ervoor dat de uitgangsspanning en -stroom van de lader overeenkomen met de specificaties van de batterij.
- Vermijd overladen: Stop op tijd met opladen en laad de accu niet boven de maximale spanning op.
- Zorg voor een geschikte bedrijfstemperatuur: Zorg ervoor dat de batterij binnen een ideaal temperatuurbereik functioneert en vermijd gebruik in omgevingen met hoge temperaturen, vooral bij extreme hitte.
- Gebruik een batterijbeheersysteem (BMS):Een BMS helpt bij het bewaken van de laad- en ontlaadprocessen, zodat de batterij binnen veilige parameters functioneert en oververhitting wordt voorkomen.
- Controleer regelmatig de conditie van de batterijControleer regelmatig het uiterlijk en de prestaties van de batterij, zodat u verouderde of beschadigde batterijen tijdig kunt identificeren en vervangen.
- Zorg voor goede ventilatie: Zorg ervoor dat het apparaat waarin de batterij zich bevindt, voldoende warmteafvoercapaciteit heeft om oververhitting te voorkomen.
Hoe om te gaan met oververhitting van de batterij
Als een batterij oververhit raakt, moeten de volgende maatregelen worden genomen:
- Schakel de stroom uit: Als de batterij oververhit raakt tijdens het opladen of gebruiken, stop dan onmiddellijk met het gebruik en haal de stekker uit het stopcontact.
- Koel de batterij af: Plaats de batterij op een schaduwrijke, geventileerde plaats en vermijd blootstelling aan hoge temperaturen.
- Controleer de batterijControleer op schade, zwelling of lekkage. Als de batterij beschadigd is, gooi deze dan op een veilige manier weg.
- Vermijd contact: Als de batterij ernstig oververhit is of rookt, vermijd dan direct contact met de batterij en houd de batterij uit de buurt van ontvlambare materialen.
Welke batterijen raken sneller oververhit?
Verschillende soorten batterijen hebben verschillende gevoeligheid voor oververhitting. Over het algemeen geldt:
18650 cilindrische NCM- en LCO-batterijen:
Deze batterijen zijn gevoeliger voor oververhitting vanwege het gebruik van nikkel-kobalt-mangaan (NCM) en lithium-kobaltoxide (LCO) chemicaliën, vooral bij hoge vermogensafgifte of in omgevingen met hoge temperaturen.
LFP (Lithium-ijzerfosfaat) batterijen:
LFP-batterijenhebben een betere thermische stabiliteit en de kans op oververhitting is lager dan bij NCM- en LCO-batterijen.
Grote prismatische batterijen (bijvoorbeeld die worden gebruikt in accupakketten voor elektrische voertuigen) kunnen ook gevoeliger zijn voor oververhitting, vooral als ze niet over een goed koelsysteem beschikken.
Waarom worden ongebruikte batterijen warm?
Zelfs wanneer de batterij niet in gebruik is, kunnen er interne chemische reacties in de batterij optreden, wat kan leiden tot hitteaccumulatie. Met name wanneer batterijen langdurig worden opgeslagen, niet volledig opgeladen of ontladen zijn, of in een warme omgeving worden bewaard, kan interne weerstand de temperatuur doen stijgen.
Kan oververhitting van de batterij leiden tot thermische runaway (TR)?
Ja, als oververhitting niet snel wordt aangepakt, kan dit leiden tot thermische runaway (TR). Dit is een extreem gevaarlijk proces waarbij interne chemische reacties intensiveren, waardoor de temperatuur snel stijgt en brand of een explosie kan veroorzaken.
Hebben batterijen van verschillende groottes invloed op de warmteafvoer?
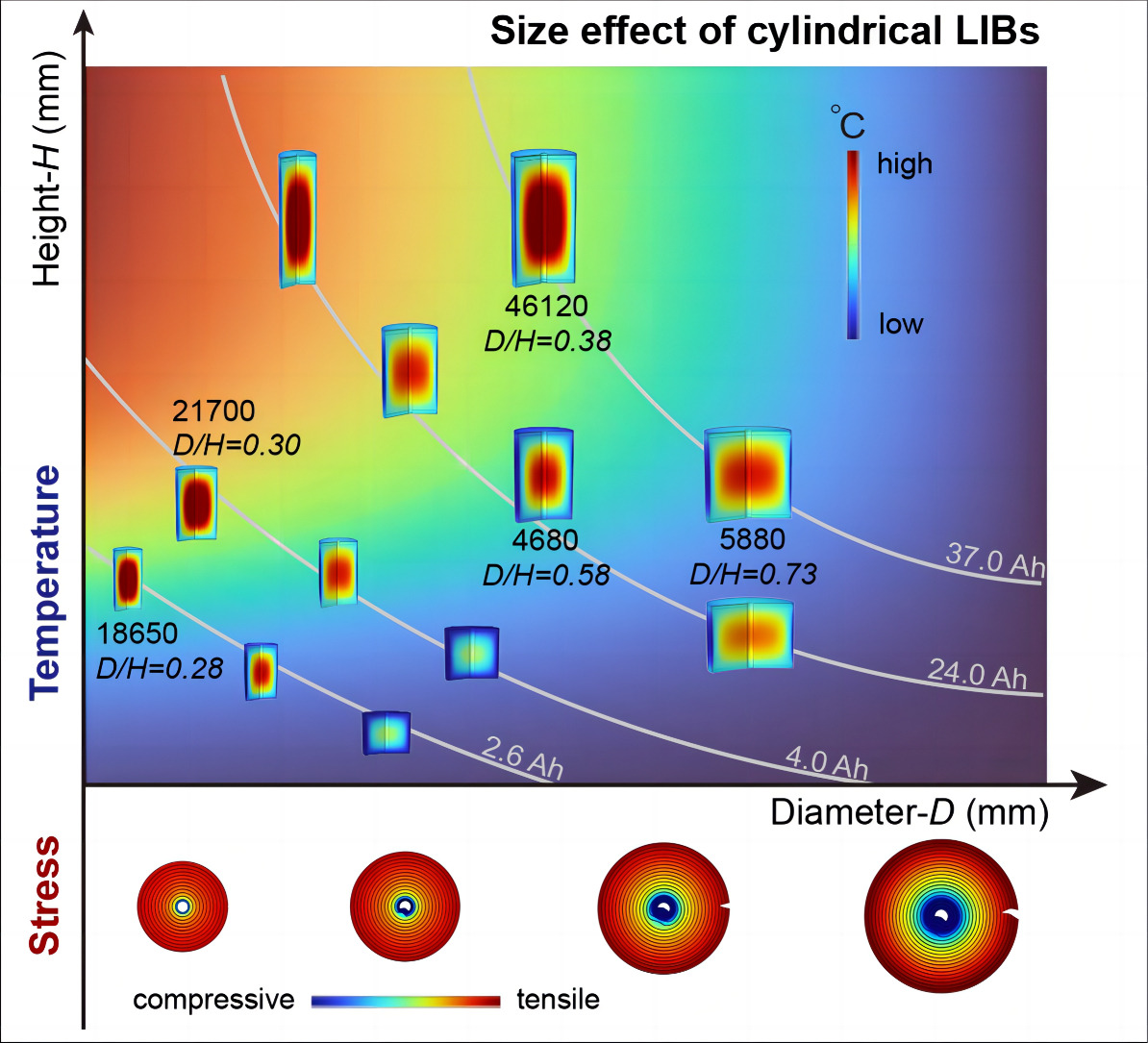
Volume beïnvloedt temperatuuroverdracht. Wanneer we bijvoorbeeld een oven of magnetron gebruiken om verschillende hoeveelheden voedsel gedurende dezelfde tijd te verwarmen, zal de kerntemperatuur van het grotere voedsel lager zijn. Op dezelfde manier wordt de warmte die wordt gegenereerd door de interne chemische reactie van de batterij van binnen naar buiten overgedragen, en batterijen met verschillende volumes zullen verschillend presteren. In Jin Liu'sonderzoek naar de relatie tussen de grootte van de cilindrische batterij en thermische prestatieswerd onthuld dat cellen met een grotere diameter-hoogte (D/H) lagere temperaturen en kleinere thermische gradiënten vertoonden.
Conclusie
Oververhitting van accu's is een probleem dat serieus moet worden genomen, vooral bij apparaten met een hoog vermogen en elektrische voertuigen. Inzicht in de oorzaken en symptomen van oververhitting van accu's en het nemen van passende preventieve maatregelen kan de levensduur van de accu effectief verlengen en de veiligheid verbeteren. Correct opladen, bewaren, gebruiksomgeving en tijdige inspectie en onderhoud zijn essentieel om oververhitting van de accu te voorkomen.
Plaatsingstijd: 12-12-2024